|
Air Conditioning System Basics and Theories
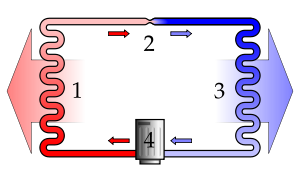 A simple stylized diagram of the refrigeration cycle: 1) condensing coil, 2) expansion valve, 3) evaporator coil, 4) compressor.
A simple stylized diagram of the refrigeration cycle: 1) condensing coil, 2) expansion valve, 3) evaporator coil, 4) compressor.
Make your air conditioner Energy Efficiency & Safety
Each air conditioner has an energy-efficiency rating that lists how many Btu per hour are removed for each watt of power it draws. For room air conditioners, this efficiency rating is the Energy Efficiency Ratio, or EER. For central air conditioners, it is the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio, or SEER. These ratings are posted on an Energy Guide Label, which must be conspicuously attached to all new air conditioners. Many air conditioner manufacturers are participants in the voluntary EnergyStar® labeling program (see Source List in this publication). EnergyStar-labeled appliances mean that they have high EER and SEER ratings.
In general, new air conditioners with higher EERs or SEERs sport higher price tags. However, the higher initial cost of an energy-efficient model will be repaid to you several times during its life span. Your utility company may encourage the purchase of a more efficient air conditioner by rebating some or all of the price difference. Buy the most efficient air conditioner you can afford, especially if you use (or think you will use) an air conditioner frequently and/or if your electricity rates are high.
Regular Maintenance
An air conditioner's filters, coils, and fins require regular maintenance for the unit to function effectively and efficiently throughout its years of service. Neglecting necessary maintenance ensures a steady decline in air conditioning performance while energy use steadily increases.
Air Conditioner Filters
The most important maintenance task that will ensure the efficiency of your air conditioner is to routinely replace or clean its filters. Clogged, dirty filters block normal air flow and reduce a system's efficiency significantly. With normal air flow obstructed, air that bypasses the filter may carry dirt directly into the evaporator coil and impair the coil's heat-absorbing capacity. Filters are located somewhere along the return duct's length. Common filter locations are in walls, ceilings, furnaces, or in the air conditioner itself.
Some types of filters are reusable; others must be replaced. They are available in a variety of types and efficiencies. Clean or replace your air conditioning system's filter or filters every month or two during the cooling season. Filters may need more frequent attention if the air conditioner is in constant use, is subjected to dusty conditions, or you have fur-bearing pets in the house.
What you should not do
- Do not overcool the room
- Avoid high heat load in the room
- Do not block the outdoor unit
- Do not install your air-conditioner's piping exceeding the recommended length
- Do not pull out the power cord when the power is on
- Do not attempt to replace blown fuse with a metal wire or the like
- Do not put heating apparatus too close to the air-conditioner
|
What you should do
- Service and maintain your air-conditioner regularly
- Set the thermostat between 22° C - 26° C for optimum comfort
- Keep the room temperature uniform
- Turn on the air-conditioner earlier rather than wait until the room is hot. That way, it will be easier to cool the room
- Keep the room temperature uniform
- Install indoor unit at a position where airflow is evenly distributed.
- Ensure that there is no irregularity on the power plug and socket
- Remove the power plug when the unit is not used for a long time
- Place your outdoor unit at a shady place
- Make sure your air-conditioner is protected with a starter
|
Sizing your Air Conditioners
Air conditioners are rated by the number of British Thermal Units (Btu) of heat they can remove per hour. Another common rating term for air conditioning size is the "ton," which is 12,000 Btu per hour.
The size of an air conditioner depends on:
- how large your home is and how many windows it has;
- how much shade is on your home's windows, walls, and roof;
- how much insulation is in your home's ceiling and walls;
- how much air leaks into your home from the outside; and
- how much heat the occupants and appliances in your home generate.
Installation and Location of Air Conditioners
If your air conditioner is installed correctly, or if major installation problems are found and fixed, it will perform efficiently for years with only minor routine maintenance. However, many air conditioners are not installed correctly. As an unfortunate result, modern energy-efficient air conditioners can perform almost as poorly as older inefficient models.
Be sure that your contractor performs the following procedures when installing a new central air conditioning system:
- allows adequate indoor space for the installation, maintenance, and repair of the new system, and installs an access door in the furnace or duct to provide a way to clean the evaporator coil.
- ensures there are enough supply registers to deliver cool air and enough return air registers to carry warm house air back to the air conditioner.
- installs duct work within the conditioned space, not in the attic, wherever possible.
- locates the condensing unit where its noise will not keep you or your neighbors awake at night, if possible
- verifies that the newly installed air conditioner has the exact refrigerant charge and air flow rate specified by the manufacturer.
- locates the thermostat away from heat sources, such as windows, or supply registers.
|